Analyzing the Shifts and Patterns
Divorce is a complex and deeply personal process that impacts countless individuals and families in the United States. By examining divorce trends and statistics, we gain valuable insights into marriage stability, demographic patterns, and societal shifts.
This blog delves into various divorce statistics, including the current divorce rate, factors influencing divorce rates, demographics of divorce, marital durations, trends in military marriages, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on divorce rates.
Through our exploration, we aim to illuminate the trends and insights surrounding divorce, aiding individuals, couples, and professionals in navigating the complexities of divorce in today’s society.
Understanding the Divorce Rate in the U.S.
The divorce rate in the United States is a key indicator of relationship stability and societal trends. It provides insight into the number of divorces that occur per 1,000 individuals in a given population, commonly referred to as the crude divorce rate.
This rate helps us understand the overall likelihood of divorce among married couples in a specific time period. By examining divorce rates, researchers, sociologists, and policymakers can gain valuable insights into family law dynamics, societal changes, and potential risk factors for divorce.
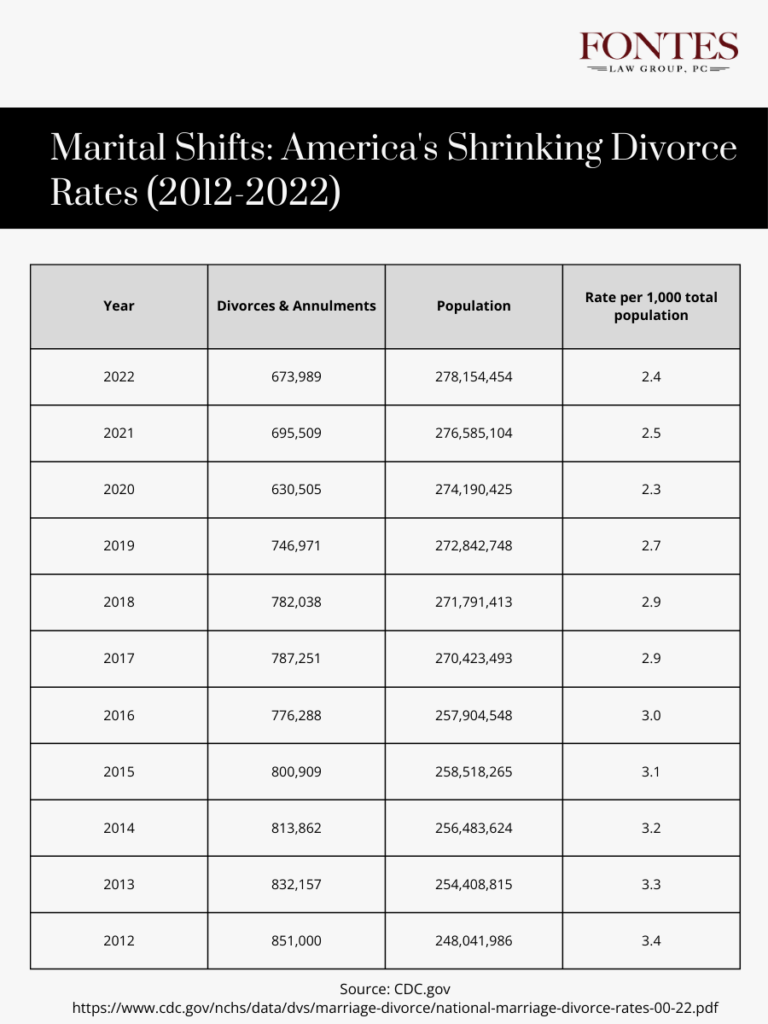
A Brief Overview of the Current Divorce Rate
The current divorce rate in the United States is 2.9 divorces per 1,000 population, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Center for Health Statistics. This rate, known as the crude divorce rate, reflects the number of divorces in relation to the total population. It provides a broad understanding of divorce trends, although it does not account for factors such as age, education, or duration of marriage.

However, experts suggest that the crude rate may not accurately represent the true divorce rate and that the rate for women, which is significantly higher, may be a more accurate statistic.
Examining divorce rates over time reveals interesting trends. For example, divorce rates have been declining in recent decades. In 1990, the crude divorce rate was 4.7 divorces per 1,000 population, significantly higher than the current rate. This decline can be attributed to various factors, including changing societal attitudes towards divorce, increased access to family planning and education, and a shift in cultural norms regarding marriage.
However, it is important to note that divorce rates can vary significantly across states and regions. For example, states like Nevada and Oklahoma have higher divorce rates, while states like Massachusetts and New York have lower rates. Socioeconomic, cultural, and demographic factors play a role in these variations, as well as differing divorce laws and support systems in different states.
Factors Influencing the Divorce Rate
Numerous factors contribute to fluctuations in the divorce rate, ranging from individual risk factors to broader societal influences. Understanding these factors is crucial for identifying potential risk factors for divorce and implementing strategies to support strong, healthy marriages.
Socioeconomic factors, such as education level, income, and occupation, play a significant role in divorce statistics. Studies have consistently shown a correlation between lower education levels and higher divorce rates. This link suggests that individuals with higher education may have better resources and support systems, both of which contribute to marriage stability.
Another important factor that influences the divorce rate is the time of marriage. Research has shown that those who marry at a younger age are more likely to divorce, while those who marry later in life have a lower divorce rate. This highlights the importance of considering the timing of marriage when examining divorce statistics.
Behavioral patterns, such as substance abuse and domestic violence, also influence the divorce rate. Substance abuse issues, including drug and alcohol addiction, can place significant strain on a marriage, leading to higher divorce rates among couples struggling with addiction. Similarly, domestic violence is a critical risk factor for divorce, as it creates an unsafe and unhealthy environment within a marriage.
Other factors, including infidelity, financial problems, and lack of communication, can contribute to divorce rates. These personal factors reflect the challenges and difficulties that couples may face in maintaining a healthy and sustainable relationship. Addressing these issues through counseling, therapy, and support services can help mitigate the risk of divorce and foster healthier marriages.

Meet Family Law Lawyer
Catherine J. Navarro
Partner
Demographics and Divorce: Who is Getting Divorced, When, and Why?
Understanding the demographics of divorce provides valuable insights into the patterns, trends, and risk factors associated with marriage dissolution. Demographic factors such as age, education level, occupation, and ethnicity play a significant role in divorce statistics, shedding light on the socio-cultural and economic dynamics that influence divorce rates. Exploring these demographics can help us better comprehend who is getting divorced, when divorces are more likely to occur, and the underlying reasons behind divorce trends.
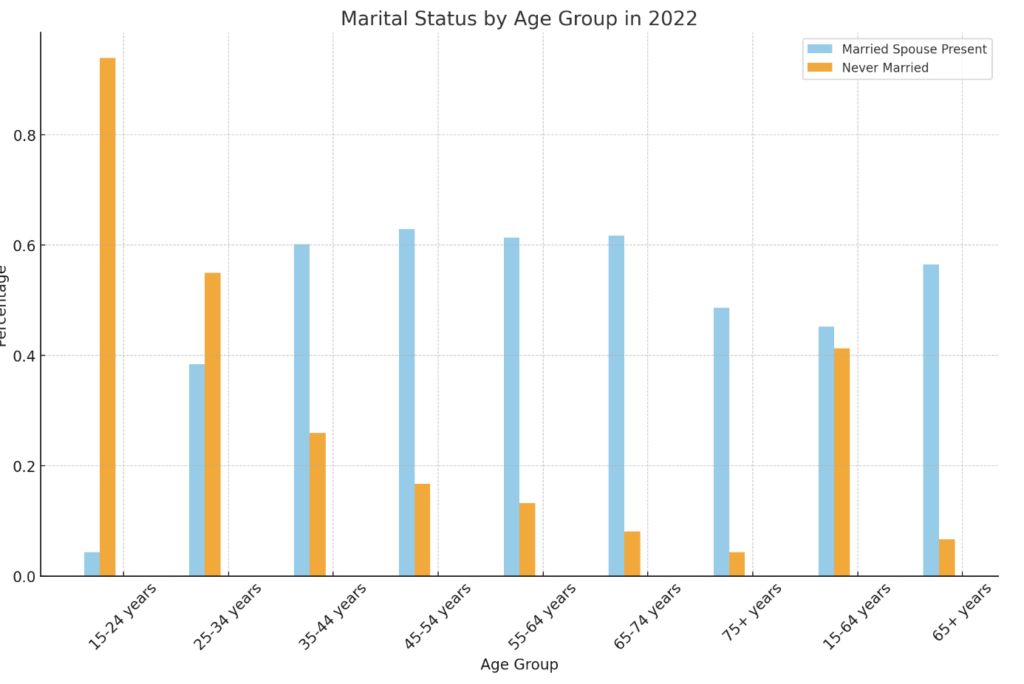
Correlation between Age and Divorce
Age is an essential demographic factor affecting divorce rates, with varying trends observed among different age groups. The average age of individuals who divorce has been increasing over the years, reflecting a shift in marriage dynamics and a potential change in societal attitudes towards divorce.
Baby boomers, those born between 1946 and 1964, have witnessed a notable rise in divorce rates, earning the label “gray divorce” generation. This increase can be attributed to a variety of reasons, including longer life expectancies, changing gender roles, financial independence, and evolving social norms.
The highest divorce rate is currently observed among individuals between the ages of 40 and 49, a period often associated with midlife crises, reevaluations of life priorities, and a desire for personal growth and fulfillment.
Understanding the correlation between age and divorce, including the most common reasons for divorce, provides valuable insights into marriage longevity, potential risk factors, and the evolving dynamics of relationships.
Impact of Education on Divorce Rates
Education level is a significant demographic factor influencing divorce rates, highlighting the relationship between educational attainment and marriage stability. Statistics consistently show that individuals with higher levels of education, such as a bachelor’s degree or higher, tend to have lower divorce rates compared to those with lower educational attainment. This correlation can be attributed to a variety of factors, including higher income levels, increased access to resources, enhanced communication skills, and a greater likelihood of marrying later in life, after establishing a stable education and career foundation.
Additionally, those with higher levels of education have a 13 percent lower risk of divorce, further emphasizing the importance of education in maintaining a stable marriage.
The impact of education on divorce rates underscores the importance of access to education, support for lifelong learning, and empowerment through knowledge, enabling individuals to build strong, healthy marriages.
Occupation and its Role in Divorce Trends
Occupation is another demographic factor that influences divorce trends, as different professions may exhibit varying divorce rates. Individuals in certain occupations may face higher levels of job-related stress, long working hours, or significant time away from family, all of which can increase the risk of divorce.
On the other hand, individuals in occupations with lower divorce rates may benefit from more flexible schedules, support systems, and a better work-life balance.
Analyzing occupation data provides insights into the unique challenges faced by couples in specific professions and highlights societal patterns in divorce trends, emphasizing the importance of fostering healthy work environments and support systems to maintain strong marriages.
Digging Deeper into Marital Durations
Examining marital durations offers a deeper understanding of the average length of marriages and provides insights into the stability of different stages of marriage. Marital duration refers to the number of years a couple has been married, which can vary significantly across individuals and demographics.
By exploring the median age of divorce and the average years of marriage before divorce, we can gain a better understanding of relationship dynamics, potential risk factors, and marriage success rates.
Median Duration of First Marriages That End in Divorce
The median duration of first marriages that end in divorce provides insight into the average length of marriages before divorce, offering a glimpse into the stability of early marriages. According to data from the American Community Survey, the median duration of first marriages before divorce is approximately 8 years. This average length of a marriage suggests that many divorces occur within the first decade of marriage, highlighting the challenges individuals and couples may face during the transition into marriage or in the early years of matrimony.
Understanding these statistics can help identify common pain points, such as communication issues, unrealistic expectations, or incompatible lifestyles, that may contribute to marriage dissolutions. By addressing these issues early on, couples may be able to strengthen their relationships and avoid the risk of divorce.
How Long do Second Marriages Last?
The duration of second marriages, also known as remarriages, is a key area of interest when examining divorce trends.
Second marriages, on average, have a slightly higher rate of divorces compared to first marriages, with studies estimating the divorce rate for second marriages at around 40-67%.
Third marriages tend to have even higher divorce rates, with estimates ranging from 73-74%.
Understanding the length of second marriages provides insights into remarriage stability, potential challenges faced in subsequent marriages, and the importance of addressing unresolved issues from previous marriages. These statistics highlight the importance of seeking support, counseling, and utilizing lessons learned from past experiences to build healthier, more resilient marriages.
Divorce Trends in Military Marriages

Military marriages face unique challenges due to the demands, uncertainties, and stresses associated with military service. Examining divorce trends in military marriages helps us gain a deeper understanding of the impact of military life on marriage stability and divorce rates.
The Unique Challenges Military Couples Face
Military couples face distinct challenges that can strain their relationships and potentially contribute to higher divorce rates. Frequent relocations, deployments, and the high-stress nature of military duties can place significant stress on marriages. Separations due to deployments and prolonged periods of being apart can impact communication, emotional bonds, and overall relationship satisfaction.
Furthermore, military couples may also face unique challenges related to domestic violence, mental health, and access to support services.
Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential in supporting strong, healthy military marriages.
Military Divorce Rates Compared to Civilian Rates
Comparing military divorce rates to civilian divorce rates provides insights into the specific challenges faced by military families and the unique circumstances that may contribute to higher divorce rates within this community.
Research suggests that military divorce rates are generally higher than civilian divorce rates, particularly during periods of increased deployment activity. These higher divorce rates can be attributed to the stress of separation, the strain of frequent relocations, and the challenges associated with managing a family while serving in the military. Policies and support structures play a crucial role in mitigating divorce rates within the military community, highlighting the significance of comprehensive family support services, mental health resources, and marriage education programs.
What Makes People More or Less Likely to Divorce?
The likelihood of divorce can vary based on a range of personal and societal factors. Understanding these influences provides valuable insight into divorce rates, trends, and risk factors, helping individuals, couples, and professionals better navigate marriage and divorce.
Personal Factors that Influence Divorce Rates
Personal factors such as substance abuse, infidelity, and cohabitation prior to marriage can significantly impact divorce rates. Substance abuse, including drug and alcohol addiction, can strain marriages, leading to higher divorce rates among couples struggling with addiction. Infidelity, a breach of trust within a marriage, also contributes to marital dissolution. Cohabitation, or living together before marriage, has become increasingly common, and research suggests a correlation between cohabitation and higher divorce rates, especially among couples with weaker religious beliefs.
These personal factors reflect the challenges and difficulties that couples may encounter, underscoring the importance of open communication, support, and counseling to prevent divorce and strengthen marriages.
Societal Influences on Divorce Rates
Societal influences, such as economic conditions and societal norms, also play a significant role in divorce rates. Economic downturns, financial strain, and unemployment can increase divorce rates, as financial stressors impact relationship dynamics. Similarly, societal norms and attitudes towards divorce can shape individual decisions and the overall divorce rate. Cultures with a higher acceptance of divorce may have higher divorce rates, reflecting a shift in social values and a reduced stigma surrounding divorce.
Understanding these societal influences helps us comprehend trends in divorce rates, highlight potential risk factors, and develop strategies to support and empower individuals and couples.
The Covid-19 Impact on Divorce Rates
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching effects on various aspects of life, including marriage and divorce trends. Examining the impact of the pandemic on divorce rates provides insights into the unique challenges faced by couples during these unprecedented times.
How the Pandemic Changed Divorce Trends
The pandemic has brought about significant changes in divorce trends. The restrictions imposed due to the pandemic, such as lockdowns, social distancing, and economic uncertainties, have placed immense pressure on relationships.
Couples have had to navigate new stressors, including working from home together, homeschooling children, financial strain, and decreased access to support systems. These unprecedented circumstances have led to a surge in divorce inquiries, with couples reevaluating their relationships amidst the challenges of the pandemic. Virtual counseling services, online divorce platforms, and remote mediation have emerged as alternative methods for couples seeking support during these challenging times.
The implications of these changes in divorce trends will continue to unfold, highlighting the importance of adapting support services, counseling, and relationship education to meet the evolving needs of individuals and couples.
Predictions for Post-Pandemic Divorce Rates
Predicting post-pandemic divorce rates is challenging, as the full extent of the COVID-19 impact on marriages and divorce trends is yet to be determined. However, experts offer some predictions based on the unique circumstances of the pandemic. Economic repercussions, such as job losses, reduced income, and financial strain, may continue to affect divorce rates in the aftermath of the pandemic.
The post-pandemic period may also see a rise in divorces as couples reassess their relationships, following a prolonged period of intense stress and uncertainty. Remote work trends, which have become more prevalent during the pandemic, may further impact divorce rates as couples navigate new dynamics in sharing physical spaces, work-life balance, and relationship satisfaction. Additionally, ongoing uncertainty and global recovery measures may lead to increased divorce filings as individuals seek a fresh start or reassess their priorities.
Does Income Level Impact Divorce Rates?
Income level is a crucial factor that can influence divorce rates, reflecting the financial stability and resources available to couples. Studies have shown a correlation between lower income levels, poverty line, and higher divorce rates. Financial strain, lack of economic security, and an inability to meet basic needs can place significant stress on marriages, potentially leading to higher divorce rates.
On the other hand, wealthier individuals may have lower divorce rates, as they often enjoy greater financial stability, access to resources, and support systems.
Understanding the impact of income level and poverty line on divorce rates underscores the importance of addressing systemic issues of poverty, providing support for families, and promoting financial literacy to support healthy, thriving marriages.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Divorce on Personal Finances?
The impact of divorce extends beyond the emotional and relational aspects, often affecting personal finances in the long run. Divorce can lead to a decrease in household income, as families separate, assets are divided, and one or both partners may face additional expenses associated with maintaining separate households.
Child support and alimony payments may also impact personal finances, with the custodial parent receiving support while the noncustodial parent contributes to child custody arrangements.
These financial obligations, along with potential legal fees, can strain post-divorce finances, highlighting the importance of careful financial planning, budgeting, and seeking professional advice to navigate the long-term effects of divorce.
Bottom Line
Diving into divorce statistics unveils a myriad of influences shaping fluctuating rates. From demographics to societal dynamics, the complexities are profound. The COVID-19 pandemic has notably impacted marital dynamics, underscoring the need for deeper comprehension. Understanding these trends offers clarity on challenges faced by couples, with far-reaching implications for families. By delving into these nuances, we gain invaluable insights shaping our perceptions of marriage, informing personal decisions, and molding societal norms. Acknowledging these trends is pivotal for nurturing healthier relationships and providing support to those navigating the intricate terrain of marriage and divorce.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are some common reasons for divorce according to recent statistics?
A: According to recent statistics, some common reasons for divorce include:
- Infidelity: Extramarital affairs and a breach of trust can severely strain a marriage.
- Substance abuse: Drug and alcohol addiction often contribute to high divorce rates, as they create significant challenges for a healthy relationship.
- Domestic violence: Physical, emotional, or verbal abuse can be a critical factor in marriage dissolution.
- Incompatible lifestyles: Fundamental differences in values, goals, or priorities can lead to ongoing conflict and a deterioration of the marriage.
- Financial issues: Money problems, excessive debt, or financial disagreements can put a significant strain on a marriage.
- Lack of communication: Poor communication, a lack of effective problem-solving skills, or an inability to resolve conflicts can erode the stability of a marriage.
Seeking counseling or therapy can help address these issues, improve marital satisfaction, and reduce the risk of divorce.
Q: Is there a correlation between certain external factors (e.g., economic conditions, societal norms) and divorce rates?
A: Yes, there is a correlation between certain external factors and divorce rates, providing valuable insights into societal trends and divorce dynamics. Some notable correlations include:
- Economic conditions: Economic downturns, high unemployment rates, or financial strain can increase divorce rates, as financial stressors significantly impact relationship dynamics. Economic stability, secure employment, and access to resources contribute to marriage stability.
- Societal norms: Attitudes towards divorce vary across cultures, communities, and time periods, influencing divorce rates. Societal norms regarding marriage, family support, and divorce acceptance can shape divorce trends. Changing societal attitudes towards divorce have led to increased divorce rates, as divorce becomes more socially acceptable and less stigmatized.
- Education level: Higher education levels are generally associated with lower divorce rates, suggesting a correlation between education, resources, and marriage stability. Higher education equips individuals with better problem-solving skills, communication abilities, and access to support systems.
- Access to support services: The availability of legal, counseling, and support services can impact divorce rates, as individuals facing marital challenges seek professional assistance. Supportive systems that provide access to mediation, counseling, and legal resources may help couples navigate marital difficulties and prevent divorce.
Understanding these correlations provides valuable insight into divorce trends, allows for the development of targeted support services, and reinforces the importance of social, economic, and cultural support structures in maintaining strong, healthy marriages.
Q: Are there any notable trends in divorce rates over the past decade?
A: Yes, there have been notable trends in divorce rates over the past decade. Some key trends include:
- Declining divorce rates: Divorce rates have been declining in recent years, especially among younger couples. This decline can be attributed to factors such as changing societal attitudes towards divorce, increased access to education, family planning, and marriage education programs, and a shift in cultural norms surrounding marriage.
- Increased age at first marriage: Individuals are getting married later in life, leading to longer average durations of first marriages before divorce. This trend reflects a shift in societal priorities, a desire for personal growth and stability, and a focus on career and education before marriage.
- Rise in gray divorces: There has been a notable rise in “gray divorces,” divorces among older adults, particularly among baby boomers. This trend can be attributed to a longer life expectancy, changing gender roles, financial independence, and evolving social attitudes towards divorce among older individuals.
- Gender dynamics: Women have been initiating divorces at higher rates than in previous years, a reflection of increased financial independence, changing cultural norms, and greater access to support systems for women facing marital challenges.
- Regional variations: Divorce rates vary significantly across states, reflecting differences in socioeconomic factors, marriage and divorce laws, and cultural norms. Some states have higher divorce rates, such as Nevada and Oklahoma, while others have lower rates, such as Massachusetts and New York.
Understanding these trends provides insights into evolving marriage dynamics, demographic shifts, and cultural influences on divorce rates over time.
